Sickle-cell anemia is a form of sickle-cell disease in which there is homozygosity for the mutation that causes HbS. Sickle-cell anaemia is also referred to as “HbSS”, “SS disease”, “haemoglobin S” or permutations of those names. In heterozygous people, that is, those who have only one sickle gene and one normal adult haemoglobin gene, the condition is referred to as “HbAS” or “sickle cell trait”. Other, rarer forms of sickle-cell disease are compound heterozygous states in which the person has only one copy of the mutation that causes HbS and one copy of another abnormal haemoglobin allele. They include sickle-haemoglobin C disease (HbSC), sickle beta-plus-thalassaemia (HbS/β+) and sickle beta-zero-thalassaemia (HbS/β0).
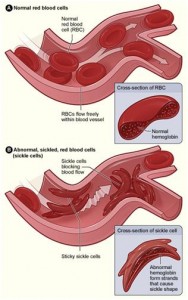
SCD is a serious disorder in which the body makes sickle-shaped red blood cells. “Sickle-shaped” means that the red blood cells are shaped like a crescent.
Normal red blood cells are disc-shaped and look like doughnuts without holes in the center. They move easily through your blood vessels. Red blood cells contain an iron-rich protein called hemoglobin. This protein carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Sickle cells contain abnormal hemoglobin called sickle hemoglobin or hemoglobin S. Sickle hemoglobin causes the cells to develop a sickle, or crescent, shape. Sickle cells are stiff and sticky. They tend to block blood flow in the blood vessels of the limbs and organs. Blocked blood flow can cause pain and organ damage. It can also raise the risk for infection.
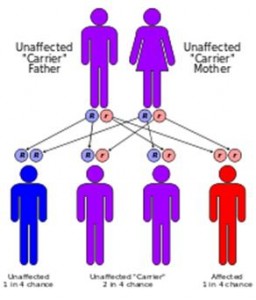
Sickle-cell conditions have an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance from parents.This is similar to the mechanism in which blood type, hair color and texture, eye colour, and other physical traits are inherited from biological parents. The types of haemoglobin a person makes in the red blood cells depend on what haemoglobin genes are inherited from her or his parents. If one parent has sickle-cell anaemia (SS) and the other has sickle-cell trait then there is a 50% chance of a child’s having sickle-cell disease and a 50% chance of a child’s having sickle-cell trait. When both parents have sickle-cell trait a child has a 25% chance of sickle-cell disease, 25% will not carry any sickle cell alleles, and 50% will have the heterozygous condition, as shown in the diagram.